In the fast-paced world of design, grasping your audience’s needs is crucial for crafting impactful solutions. One valuable tool for bridging the gap between users’ needs and your design process is customer empathy mapping. But what exactly is empathy mapping?
In this blog, we’ll explore the definition of empathy mapping, its key components, and how to create an empathy map, complete with examples. Whether you’re an experienced UX professional or just starting out, mastering empathy mapping can significantly enhance your ability to create meaningful and effective user experiences.
Definition of an Empathy Map
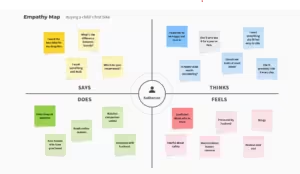
An empathy map is a collaborative visualization tool that enhances your understanding of a user’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It enables teams to gain insights into users’ experiences and perspectives, ultimately informing product development and design choices. By mapping these elements, teams can empathize with users, pinpoint their pain points, and develop solutions that align with user needs.
Elements of an empathy map
An empathy map consists of four main quadrants, each representing a different aspect of the user’s experience:
Says
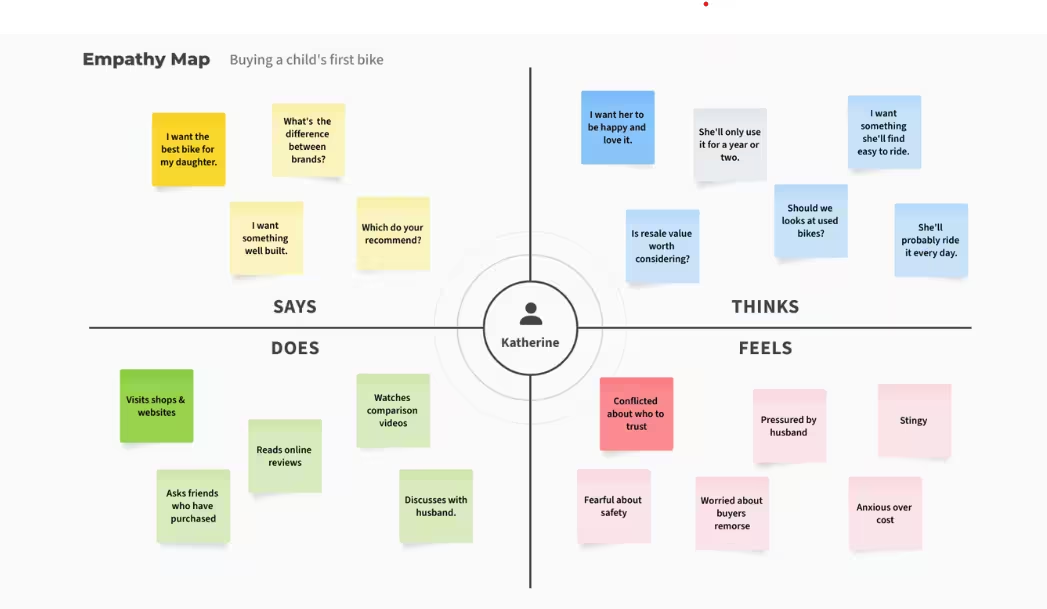
The “Says” quadrant records direct quotes or statements from users, including insights gathered during interviews, surveys, or user testing. It offers a clear view of what users articulate, highlighting their immediate concerns, desires, and thoughts.
Thinks
The “Thinks” section delves into the internal thoughts and beliefs of the user. It captures what users may be contemplating or worrying about, even if they don’t vocalize it. This quadrant helps reveal the underlying motivations, concerns, and beliefs that influence user behavior.
Does
This quadrant focuses on the user’s actions and behaviors. It encompasses what users physically do, such as interacting with a product, navigating a website, or completing tasks. Observing these actions can uncover patterns, usability issues, and areas for product or service improvement.
Feels
The “Feels” quadrant captures the emotional responses of the user. It includes the emotions experienced during interactions with the product or service, such as frustration, satisfaction, confusion, or joy. Understanding these emotions is essential for designing experiences that resonate with users on an emotional level.
Empathy maps in UX design
Empathy maps play a vital role in UX design by offering a visual and structured approach to understanding users’ perspectives. By capturing users’ thoughts, feelings, actions, and spoken words, empathy maps provide a holistic view of the user experience. This tool helps identify key pain points, motivations, and unmet needs, enabling teams to create more user-centered and empathetic designs.
Additionally, empathy maps enhance communication and collaboration within design teams, ensuring everyone shares a common understanding of the user. This unified perspective is essential for making informed design decisions, prioritizing features, and ultimately developing products and services that resonate with users and effectively address their needs and concerns.
When to Use an Empathy Map
- In the Early Design Process
Utilize empathy maps at the outset of the design process to build a foundational understanding of your target users. This initial insight guides user-centered design and ensures decisions are based on a clear grasp of user needs. - Design and Ideation Phase
Empathy maps are essential for generating and refining ideas during the design and ideation phase. They offer a detailed view of users’ experiences, helping teams brainstorm solutions that effectively address user pain points and desires. - Improving Existing Products
When enhancing an existing product, empathy maps can pinpoint areas for improving the user experience. Understanding current user frustrations and needs allows for targeted adjustments that better meet expectations. - Product Launch Analysis
After launching a product, empathy maps can analyze user feedback and behavior. This evaluation helps assess how well the product meets user needs and identifies opportunities for further enhancements. - Customer Journey Mapping
Empathy maps complement customer journey mapping by offering deeper insights into the emotional and psychological aspects of user interactions. They help visualize the entire user journey, ensuring each touchpoint addresses genuine user needs and concerns.
How to create an empathy map
Steps to Create an Empathy Map
Iterate and Update
An empathy map is a dynamic tool that should be regularly updated as you gather more data or as user needs evolve. Iterating on the map ensures it remains relevant and continues to provide valuable insights throughout the design process.
Define the User
Begin by clearly defining your user. Develop a detailed user profile or persona that includes demographic information, roles, goals, and challenges. This focus ensures your empathy map is relevant to the right audience.
Gather Data
Collect both qualitative and quantitative data about your users through interviews, surveys, observations, and feedback. This data serves as the foundation for understanding users’ experiences, thoughts, and emotions.
Set Up the Empathy Map
Create a large visual template divided into four quadrants: Says, Thinks, Does, and Feels. This template can be physical (like a whiteboard) or digital (using design tools). Clearly label each quadrant for effective organization.
Fill in the Quadrants
Populate each quadrant with the collected data. In the “Says” section, note what users express, while the “Thinks” quadrant captures their internal thoughts. Record actions in “Does” and emotions in “Feels.” Use direct quotes and observations to accurately reflect the user experience.
Collaborate and Validate
Work with your team to review and refine the empathy map. Share findings and discuss insights to ensure the map accurately represents the user experience. Validate the information with real user feedback for confirmation.
Analyze and Use Insights
Analyze the completed empathy map to identify key patterns, pain points, and opportunities. Use these insights to inform design decisions, prioritizing features that address the most critical user needs.
Conclusion
Empathy mapping is an essential UX design tool that helps understand users by capturing their thoughts, feelings, actions, and statements. This comprehensive view enables the creation of user-centered designs that effectively address real needs and enhance overall user satisfaction.